Types of Chromatography: What You Need to Know
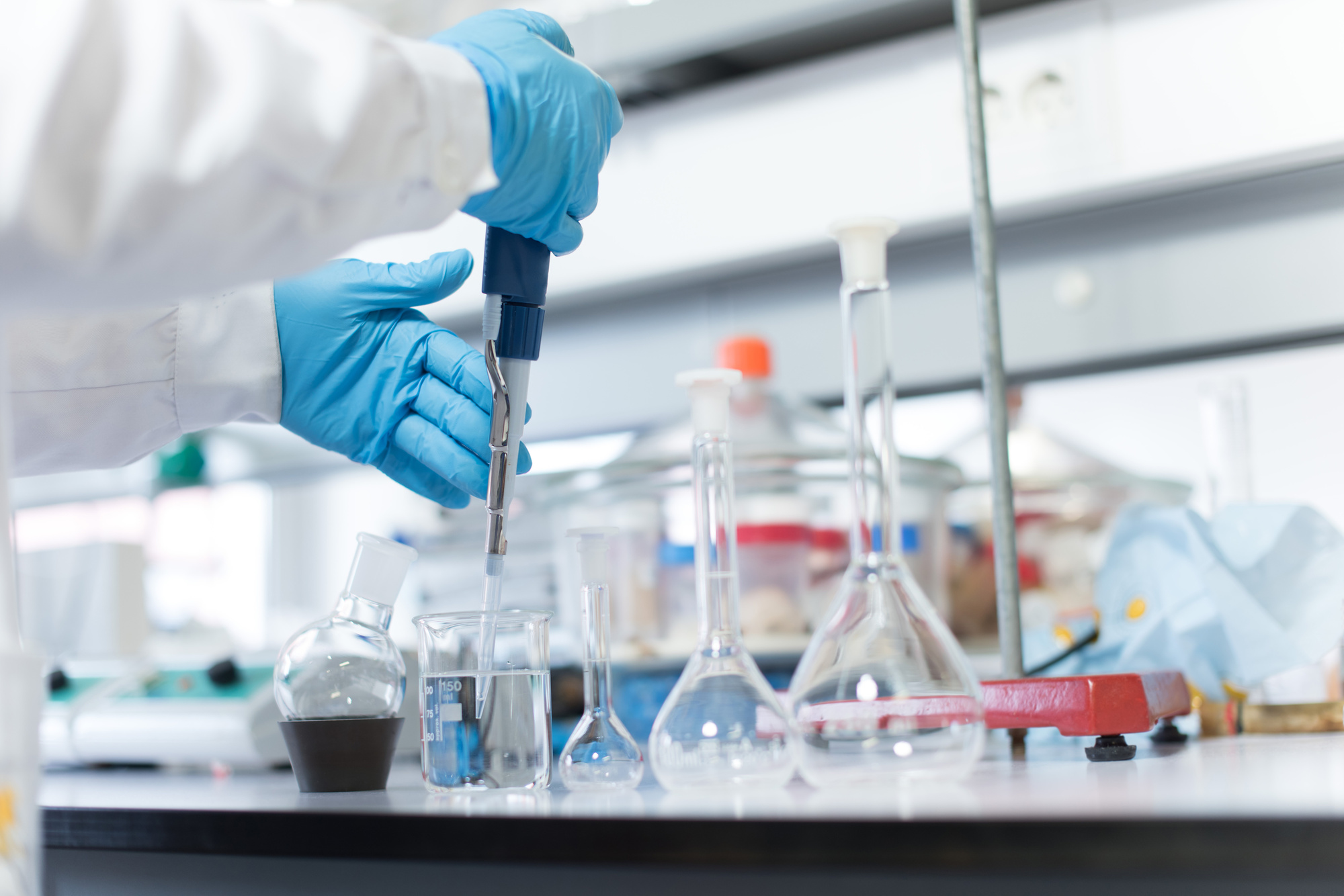
Whether you’re a chemistry student, forensic expert, or pharmacist, chromatography plays a huge part in your work and research. And while you may be an expert at using the technique, it’s always smart to refresh your memory on its many details.
What is chromatography, and how is it used in different industries? This guide takes a look at the types of chromatography and how they differ.
Flash Chromatography
Flash chromatography is a type of chromatography used to isolate and purify compounds. A column containing a stationary phase with a mobile phase of solvent is used to separate compounds.
The results can be monitored with a UV-Vis detector to monitor the compounds as they elute. Flash chromatography can be helpful. It can help when trying to separate non-volatile compounds. It can also help compounds that contain multiple functionalities.
It can also be used to separate a mixture of enantiomers or different configurations of the same compound. Flash chromatography has become increasingly popular due to its fast speed and smaller amounts of sample needed.
Affinity Chromatography
Affinity chromatography is a type of chromatography where a molecule, usually a protein, is separated. It uses its specific binding properties to a particular ligand. It is often used in biological analytics because of its high recovery rate and selectivity.
This type of chromatography is based on intermolecular interactions. This applies between the ligand molecule and the functional groups of the peptide or protein. A stationary phase with a specific ligand allows interaction with those functional groups.
To get the most out of chromatography experiments, it is important to understand the different types of chromatography. Also, get to know the significance of using an accessory at https://www.chromtech.com/96-well-plate.
Liquid Chromatography
Liquid chromatography is a type of chromatography that utilizes a mobile phase in liquid form. It works by separating the components of a mixture based on their relative affinity for the two phases.
The mobile phase consists of a solvent that completely dissolves the sample and transports it through a stationary phase. The stationary phase is a solid adsorbent material. This causes a differential interaction between the molecules of the mixture.
There are several types of liquid chromatography, including:
- high-performance liquid chromatography
- partition liquid chromatography
- normal phase chromatography
- reverse-phase chromatography
- ion exchange chromatography
Each of these variants has unique applications in the analysis of a wide variety of separation problems.
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) is a type of chromatography that combines the separation properties of gas chromatography with the properties of a liquid chromatography system.
SFC is a high-performance liquid chromatography technique. This is where you treat a compressed gas so that it will exceed its critical temperature and pressure. It also creates a fluid with properties between those of a liquid and a gas.
SFC is often used for the analysis of complex compounds. This includes proteins and polysaccharides that require ultra-high levels of resolution. SFC conserves samples and allows for automation since columns are used multiple times without a replacement.
Paper Chromatography
Paper chromatography is one of the most common types of chromatography. It separates the components of a mixture based on their solubility.
This technique is often used in chemistry, biology, and biochemistry experiments. It identifies unknown compounds. It utilizes chromatographic paper, which contains an absorbent material that holds the sample on its surface.
A solvent that passes through the paper pushes the sample through the material. This causes the components to separate based on their different rates of movement.
The components then appear as colored bands on the paper, which can be detected and identified. The sensitivity of paper chromatography depends on the following:
- size of the sample
- type of solvent
- type of chromatographic paper
It is important to select the right solvent and paper to obtain the best results.
Gas Chromatography
Chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify components of a sample. It applies to various chemical and biological sciences. There are various chromatography types based on the type of medium used- liquid, gas, and ion exchange.
Gas chromatography (GC) is used to identify and quantify volatile components in a sample. It works by passing a mixture of gases through a column filled with an inert solid or liquid material.
Traditional Chromatography
This is a technique used to separate mixtures that are often a combination of chemical compounds. This separation is due to the different solubility, polarities, and sizes of the molecules.
Traditional chromatography involves the use of an adsorbent to separate compounds based on their different characteristics and properties like:
- paper
- silica gel
- alumina
Countercurrent Chromatography
Countercurrent chromatography (CCC) is for separating small and large molecules. This method carries out in a liquid-liquid or multi-phase system. It extracts compounds from a variety of sources.
CCC gets its advantage from a mixing of two or more immiscible phases. The phases are stationary, while the mobile phase is constantly moving and exchanging with each other.
This type of chromatography is often preferred over other chromatographic techniques due to its:
- flexibility
- simplicity
- cost-effectiveness
It is especially useful when dealing with complex mixtures, such as those found in natural products.
Column Chromatography
Column chromatography involves a stationary phase in the form of a packed column. This is filled with a stationary phase (frequently a liquid or solid).
The sample mixture is on the top of the column, after which the components of the mixture are carried through the stationary phase.
As they move through the column, they interact with the stationary phase. This results in the separation of the various components.
Know All About Types of Chromatography
In conclusion, chromatography is a versatile and efficient technique. It is by chemical, biological, and other scientific fields.
Its different forms can be used to separate, identify and quantify various components of mixtures. Learn more about Types of Chromatography and their advantages to improve your laboratory work. Try it for your analytical purposes today!
Did you find this article helpful? Check out the rest of our blog for more related content.